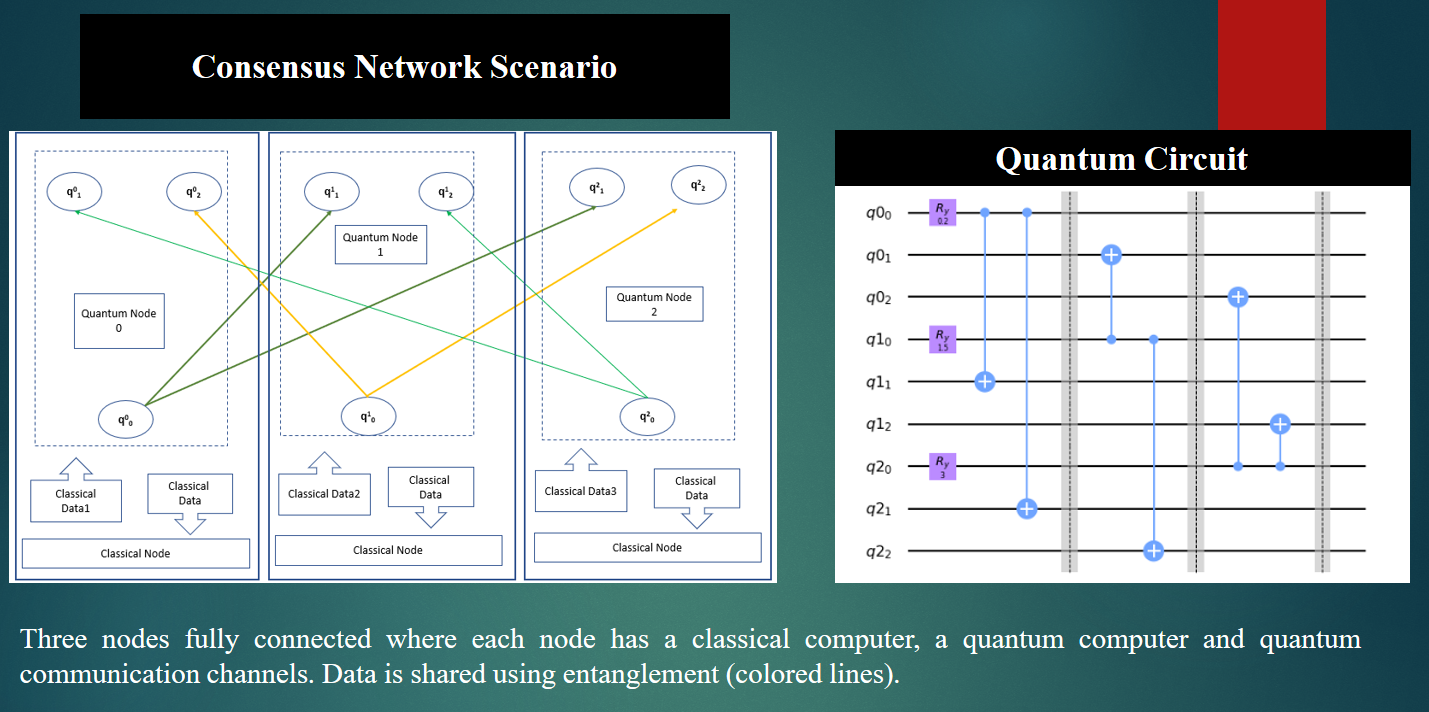
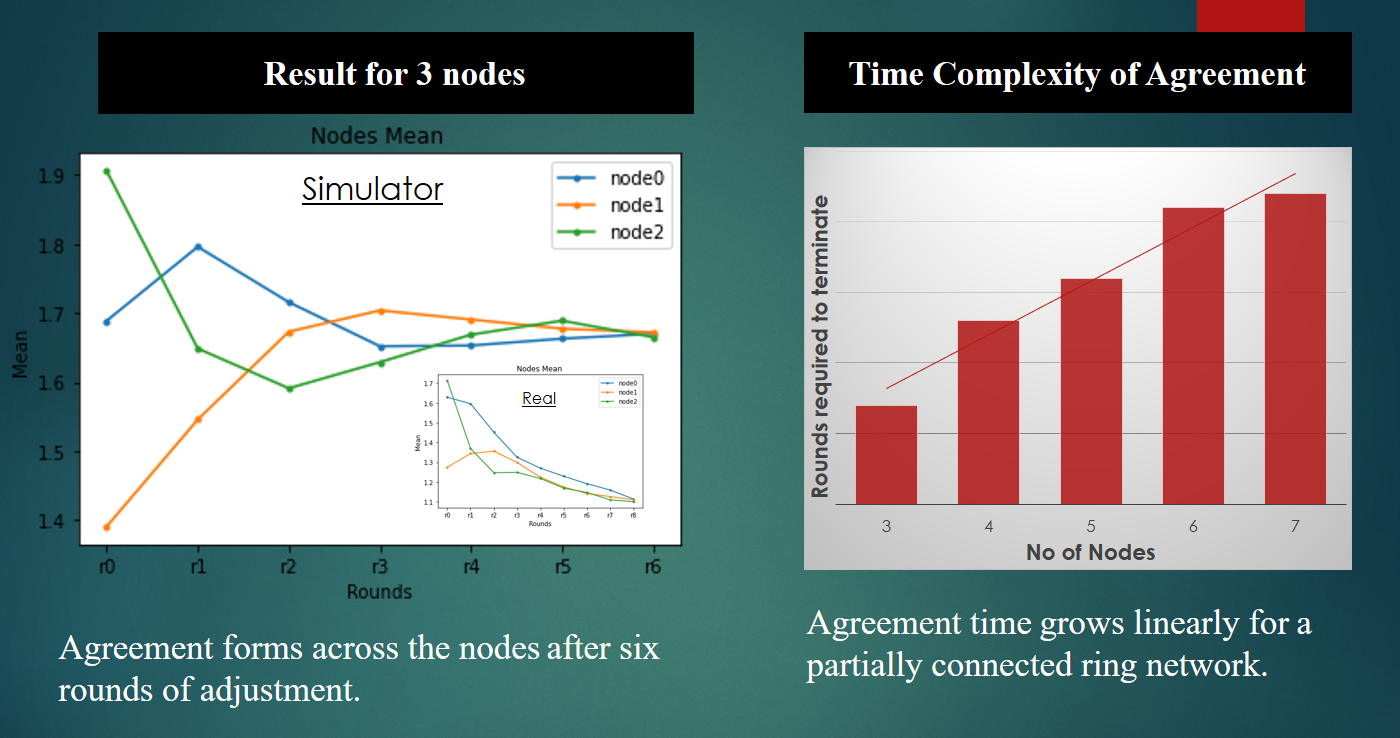
In today’s world of Distributed Ledger technology, consensus is achieved within the limitations of data size, consensus speed and network security, known as the blockchain trilemma. Quantum technologies can enhance all these three properties simultaneously using the quantum phenomena of superposition and entanglement. Here, we demonstrate a leaderless quantum consensus alogrithm using quantum simulators and real quantum computers for a simple consensus scenario.
Any IT solution that requires consensus agreement among distributed nodes and is currently constrained in size, speed or security could benefit from this technology. We are happy to hear from anyone with such needs and in particular if the data is generated by quantum sensors.
The main innovation in this technology is the use of quantum computers for the consensus algorithm along with the use of quantum communication channels. Quantum computers store data values in quantum registers that scales exponentially with the number of quantum bits (qubits) whereas current classical computer store only one value at any one time. Furthermore, the values are all processed simultaneously in parallel whereas classcial computers process serially. This gives improvements in both size and speed. Quantum computers are often discussed in terms of breaking current cryptographic algorithms but they can also create new, stronger, cryptographic systems. In summary, the key advantages and value propositions for users are the size of data that can be kept in consensus, the enhanced speed and security of data transmission.
This technology will be suitable wherever consensus is required in distributed systems, such as for the oracle problem in blockchains.
Further uses: anywhere using decentralised solutions
For blockchain alone, the global market size is expected to grow from USD 3.0 billion in 2020 to USD 39.7 billion by 2025, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 67.3% during 2020–2025. This technology will support this growth and applications can go beyond blockchain applications.
The key benefits for customers will be in having secure consensus for very large amounts of data.Costs still depends on the further development of quantum hardware as it matures over the coming years.There may be environmental benefits from using quantum resources over classical computers reducing energy costs.